Stereotactic Radio Surgery (SRS)
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) is a non-invasive surgical procedure used to treat brain disorders, primarily tumors and certain functional disorders, without the need for traditional surgery. Despite its name, it’s not actually a form of surgery in the conventional sense, as it doesn’t involve making incisions.
Here’s how it typically works:
Imaging: The process begins with high-resolution imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans to precisely locate the target within the brain.
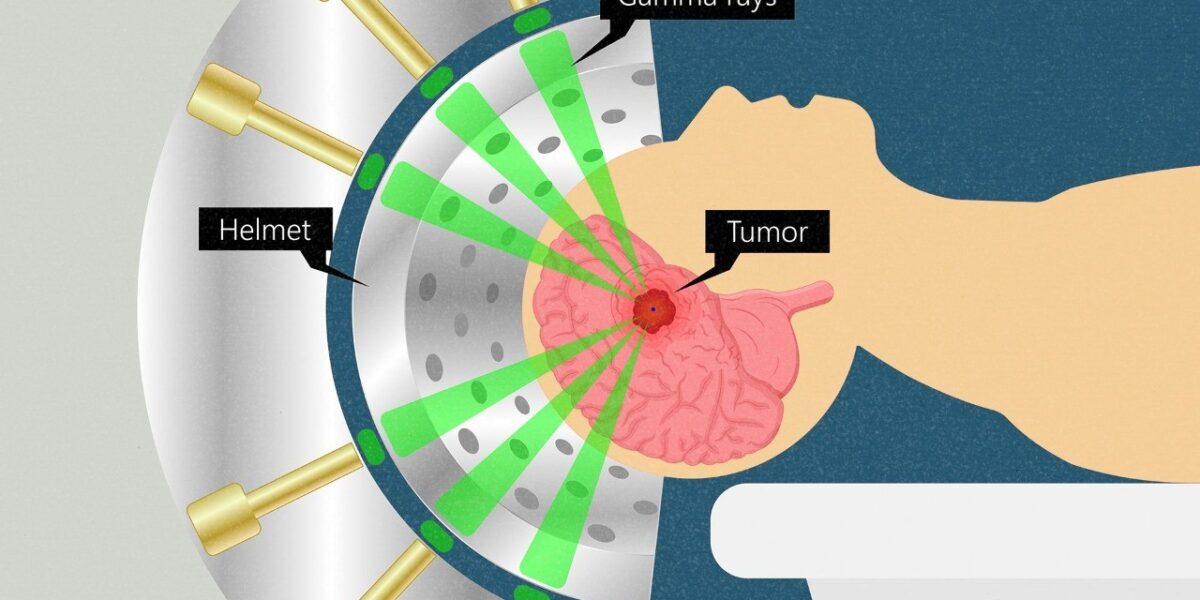
- Treatment Planning: Once the target is identified, sophisticated computer software assists in planning the treatment. This involves determining the precise dose of radiation and the angles from which it will be delivered to maximize its effectiveness while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Radiation Delivery: During the procedure, multiple highly focused radiation beams are aimed at the target from different angles, converging precisely on the affected area. Each individual beam is relatively weak, but where they intersect, they deliver a high dose of radiation, effectively destroying the target tissue.
Patient Immobilization: To ensure accuracy, the patient’s head is immobilized using a specialized head frame or mask during treatment.
Monitoring: Throughout the procedure, the patient’s position and the accuracy of radiation delivery are continuously monitored using imaging techniques like real-time MRI or CT scans.
Single or Fractionated Treatment: Depending on the condition being treated, stereotactic radiosurgery may be administered in a single high-dose session (hence the term “surgery”) or fractionated over several smaller doses delivered over several days.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is highly precise, allowing for targeted treatment while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. It’s commonly used for conditions such as:
- Brain tumors, both cancerous (malignant) and non-cancerous (benign)
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), which are abnormal tangles of blood vessels in the brain
- Trigeminal neuralgia, a chronic pain condition affecting the trigeminal nerve in the face
One of the key advantages of SRS is its non-invasive nature, meaning there’s no need for surgical incisions, anesthesia, or lengthy recovery times. However, it’s not suitable for all types of brain disorders, and its effectiveness depends on various factors, including the size and location of the target and the overall health of the patient.
